Location: Orbit of the skull.
Shape: Spherical.
Diameter: 2.5 cm (1 inch).
Structure of the eye:
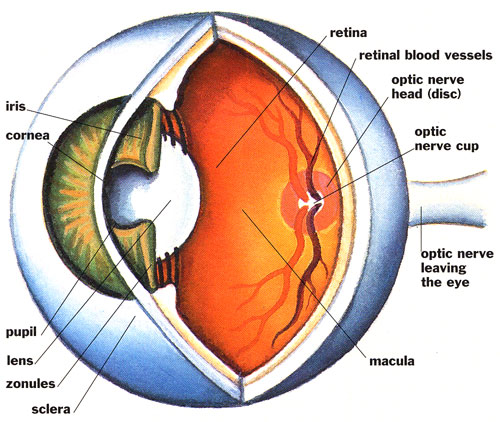
The eyeball is composed of three coats (tunics), a lens, and two principal cavities
1. Outer / fibrous coat has two parts:-
(a) The sclera is opaque and forms the posterior five-sixth of the eyeball. It is composed of dense fibrous tissue. It maintains the shape of the eyeball.
(b) The cornea is transparent and forms the anterior one sixth of the eyeball.
2. Middle / vascular coat has three parts :-
(a) The choroids, a thin pigmented layer. It is highly vascular and supplies nutrients and oxygen to the eye
(b) The ciliary body, The thickened anterior portion that encircles the lense.
(c) The iris, the most anterior portion of the vascular coat. It consists of pigment which gives the visible colour of the eye. Pupil is the round opening in the centre of the iris. It controlsthe amount of light to enter the eye.
3. Inner coat/Retina, the thin delicate inner layer of the eyeball. It is continuous with the optic nerve posteriorly.
The retina contains two types of photoreceptors:
(a) Rods can respond to dim light and are responsible for night vision.
(b) cones respond only to bright light and are sensitive to colour vision.
Layers of retina:
The retina is composed of ten layers
outer pigment layer
layer of rods and cones
external limiting membrane
outer nuclear layer
outer plexiform layer
inner nuclear layer
inner plexiform layer
ganglion cell layer
optic nerve fibres layer
internal limiting membrane